HUMAN OCCUPATION ALONG THE FOOTHILLS OF NORTHWESTERN ZAGROS DURING THE LATE PLEISTOCENE AND THE HOLOCENE IN THE RANIA AND PESHDAR PLAINS
240307025048.png)
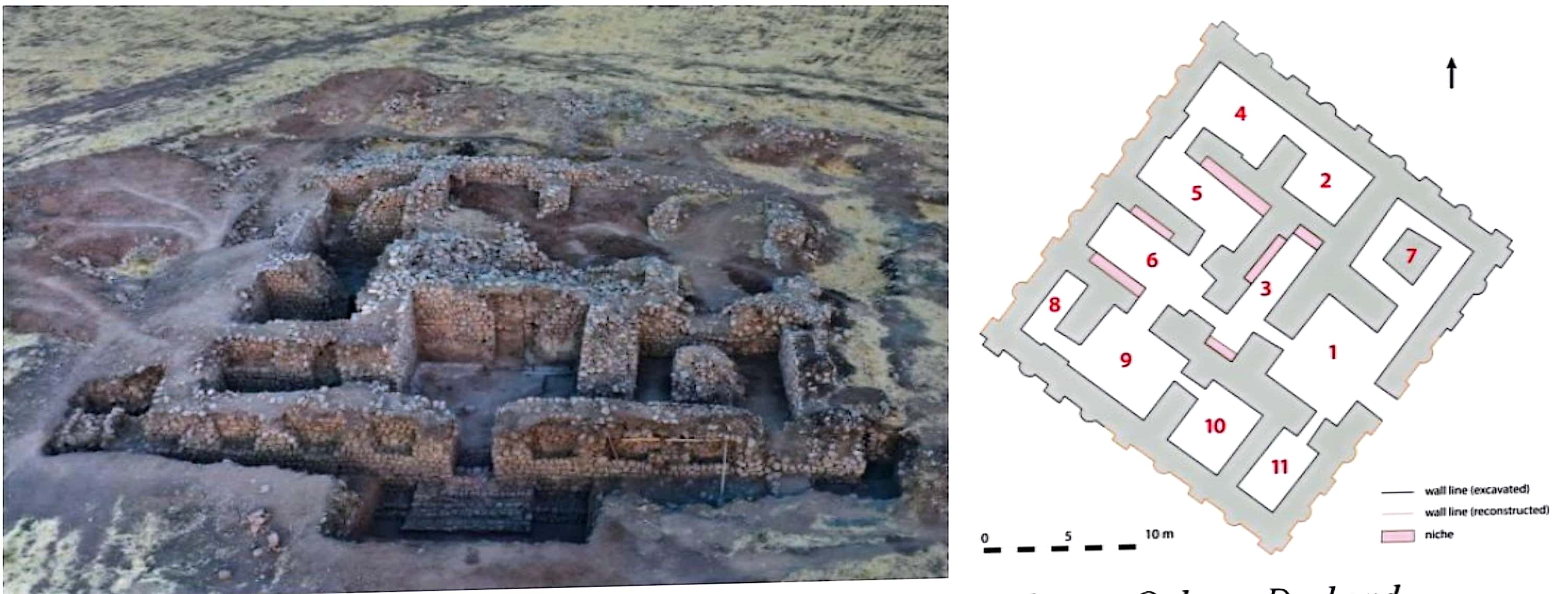
The south-western foothills of the Zagros range, in Iraqi Kurdistan, have long been largely unexplored because it has been impossible for archaeologists to carry out fieldwork research in this area for more than half a century. The first excavations carried out in the 1960s and 1970s revealed the crucial importance of the region for the prehistoric periods. Many important sites, such as Shanidar (Solecki 1963), Jarmo (Braidwood et at 1983) and Shemshara (Mortensen 1970) were discovered and excavated. Although for several decades this territory has been con-sidered a peripheral area, it is, undoubtedly, a region that is fundamental for the understanding of the first Mesopotamian cultures. In fact, this area spawned the emergence, develop-ment and spread of major cultural entities, from the Neanderthal hunter-gatherers to the first complex societies characterised by the very large villages of the Late Chalcolithic period.

240128080157.png)