Issue 18
Issue 18
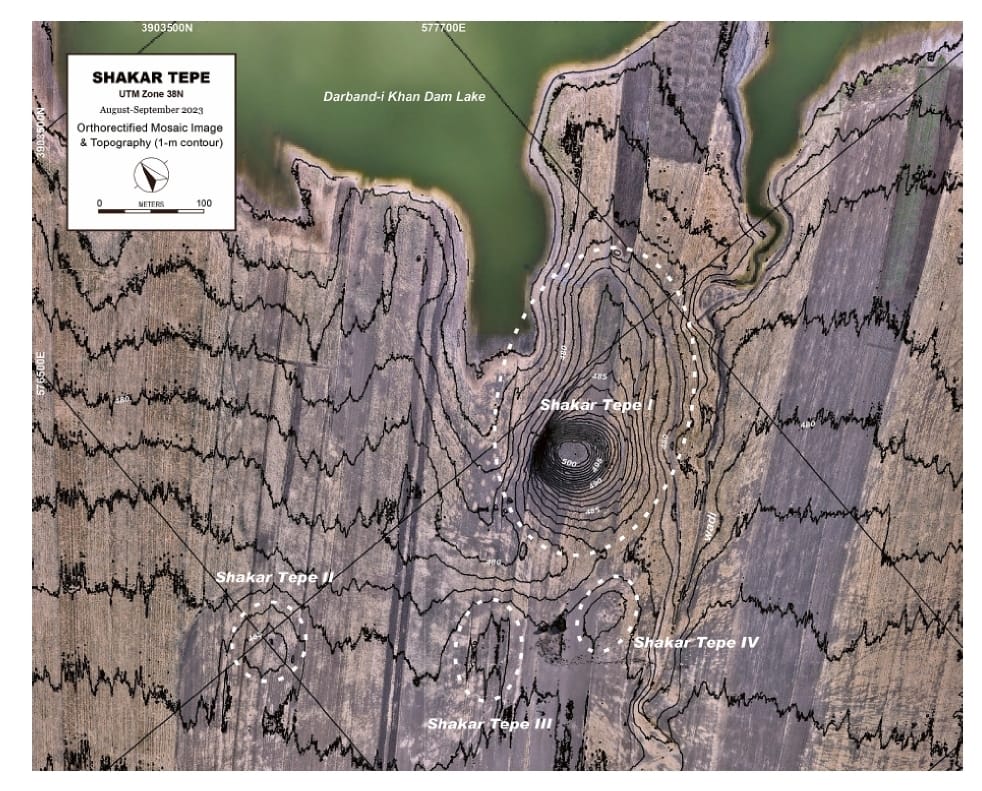
The Shahrizor Plain is one of the ideal fields for tracking the transition from Neolithic village life in the Fertile Crescent to Urbanisation which occurred in Mesopotamia because of its geographical location connecting the mountainside valleys along the Zagros and the downstream Diyala River that flows into the Tigris. Our field project aims to obtain archaeological materials to unveil this process. Following the first excavations at Shakar Tepe conducted in 2019, we excavated two additional areas at this site in 2023, including one of the three satellite mounds that were newly identified around the main mound. The cultural remains of the Late Halaf settlement uncovered from Operation B at Shakar Tepe II date back to approximately 5600–5400 calBC. On the other hand, Operation C at Shakar Tepe I yielded a thick deposit of the Late Chalcolithic occupations dated to ca. 3800–3600 calBC. The recovered materials fill the time ranges in the late prehistoric chronology of the site and will contribute to our understanding of the historical role of this region in the transition from Neolithisation to Urbanisation.
240111034934.jpg)
In the Chwartaq district, there is a residential project. As per the Guidelines for the Implementation of the Law on The Management and Preservation of Heritage the Kurdistan Region of Iraq No. 5 of 2021, which were published in Al-waqa'a Al-iraqiya Newspaper (306), Number (23) on 14/7/2023, Article (10) and paragraph (3) state that if the land area for a commercial project exceeding more than (10 Acres), a test pit needs to be excavated to determine if the land is an archaeological site or not.
Issue 18