Issue 24
Issue 24
240128075940.png)
In the late third and early second millennium bc, the large plain known today as the Shahrizor and its surrounding region, located in the province of Suleymaniyah in Iraqi Kurdistan, likely formed an important region of the kingdom of Simurrum (Fig. 31.1; Altaweel et al. 2012). For much of the remaining second millennium bc and into the irst two centuries of the irst millennium bc, the region was a contested border zone between northern and southern Mesopotamian kingdoms or became splintered into small kingdoms.
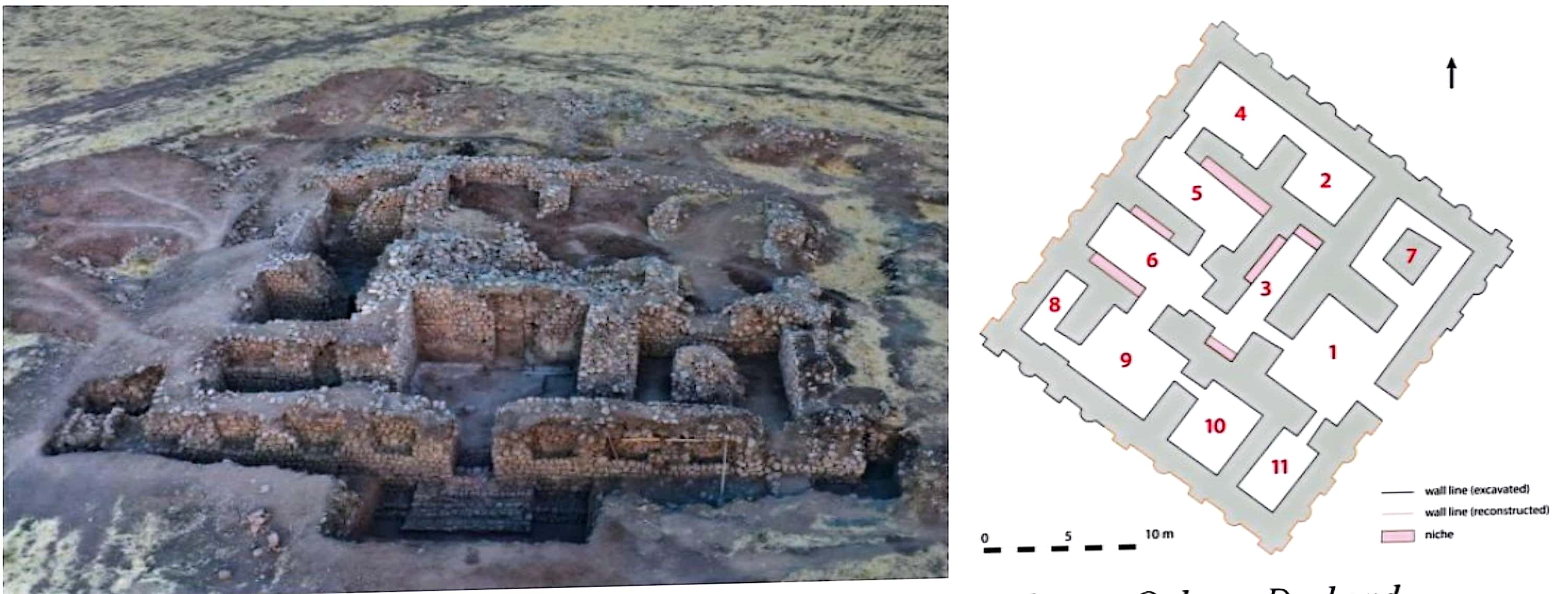
Darband-i Rania Archaeological Project the Darband-i Rania Archaeological Project was a project directed by Dr. John MacGinnis of the British Museum, carried out in co-operation with the General Director of Antiquities of Kurdistan, the Directorate of Antiquities and Heritage of Raparin and the Directorate of Antiquities and Heritage of Slemani.
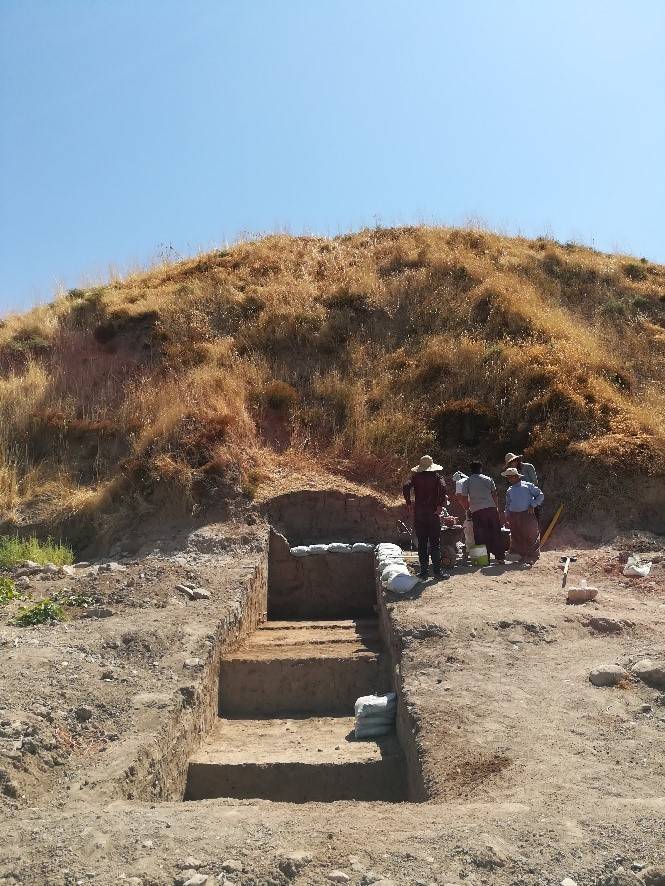

Shakar Tapa has been known as a conspicuous archaeological site in the south of the Shahrazor Plain since the mid-20th century. It has an oval plan consisting of a low northeastern mound and a high conical southwestern mound with a flat top.
Issue 24